Quantifying free-living sedentary behaviour using activity monitors
Assessing physical activity
Quantifying physical activity, or lack thereof, have been used to analyse sedentary behaviour in order to understand physical activity and disease outcomes, as well as define the effectiveness of intervention strategies. Physical activity has previously been assessed by means of self-reported measures such as questionnaires and interviews, especially in larger population studies. However, such self-reported measures can report bias in the study. With advancement in technology, wearable activity monitors are increasingly being used to objectively quantify free-living sedentary behaviour. Furthermore, they are generally small, lightweight, portable, non-invasive and unobtrusive.
The study
A recent large population study (2,497 individuals) published in the journal Diabetologia on 2 February 2016 (1) was one of such studies undertaken to measure free-living sedentary behaviour using wearable activity monitors. The study, led by first author Julianne van der Berg and senior author Annemarie Koster from Maastricht University, looked at the amount and patterns of sedentary (sitting or reclining) behaviour in relation to type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. It was performed within The Maastricht Study, an extensive phenotyping study of adults that focuses on the etiology of type 2 diabetes and its complications and comorbidities.
Results
The study participants with Type 2 Diabetes spent less time stepping and had less moderate intensity activity but the most significant risk factor is the increased time spent sedentary (sitting/lying). It was concluded that an extra hour of sedentary time was associated with a 22% increased risk for type 2 diabetes and 39% increased risk for the metabolic syndrome. These results suggested that sedentary behaviour may play a significant role in the development and prevention of type 2 diabetes.
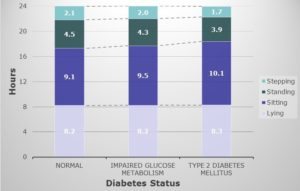
Fig. 1 Time (hours) spent in primary daily activities according to glucose metabolism status. (Adapted from van der Berg et al., 2016) (1)
Activity monitors
There are activity monitors that have been developed for research purposes and more specifically, for accurately distinguishing sedentary behavior. The Glasgow-based PAL Technologies’ activPAL™ activity monitor was chosen by the researchers in the Maastricht Study. Similarly, the MOX activity monitor has proven high accuracy in determining free-living physical activity behavior and assessing different activity intensities in healthy and chronically ill patients (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, type 2 diabetes or mitochondrial disease) (2, 3). Furthermore, the MOX activity monitor is waterproof and can be adhered directly to the skin on the thigh 24/7 for 8 days by a patch. Using accurate, reliable and objective activity monitors is an advantage as advances in accelerometry technology have allowed low power consumption, easy setup, and unobtrusive design to provide a promising tool for monitoring free-living physical activities.
Click here to the article by van der Berg et al. published online in the journal Diabetologia, 2016.
REFERENCES
- van der Berg JD, Stehouwer CDA, Bosma H, van der Velde JHPM, Willems PJB, Savelberg HHCM, et al. Associations of total amount and patterns of sedentary behaviour with type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: The Maastricht Study. Diabetologia. 2016;59(4):709-18.
- van der Weegen S, Essers H, Spreeuwenberg M, Verwey R, Tange H, de Witte L, et al. Concurrent Validity of the MOX Activity Monitor Compared to the ActiGraph GT3X. Telemedicine and e-Health. 2015;21(4):259-66.
- Koene S, Dirks I, van Mierlo E, de Vries PR, Janssen AJWM, Smeitink JAM, et al. Domains of Daily Physical Activity in Children with Mitochondrial Disease: A 3D Accelerometry Approach. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 1-11.
For more information about The Maastricht Study:
https://www.demaastrichtstudie.nl/research
For further information about the Maastricht Study, please contact :
 Anniemarie Koster
Anniemarie Koster
Associate Professor
Associate Professor Programme: Inequity, Participation and Globalisation (IPG)
Sociale Geneeskunde, School for Public Health and Prim Care, Fac. Health, Medicine and Life Sciences
Exercise Does Not Negate the Harmful Effects of Inactivity
Exercise is healthy, but an hour per day cannot fully compensate for the negative effects of excessive sitting and inactivity during the rest of the day.
It is generally known that exercise is beneficial for health and in reducing the risk of metabolic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Unfortunately, many adults do not reach the current physical activity guidelines (150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week). Moreover, we sit too much. In the car/bus on the way to work, at work behind our desk and at home in front of the television or computer. Inactivity, especially excessive sitting, is a major implicator of metabolic diseases and has been branded the “new smoking” for its supposed health risks. Whether this statement is true is inconclusive based on current research, but one thing most researchers do agree: too much sitting is unhealthy.
Decreasing sitting time by moving more and fitting physical activity into your day is one way to get started. Other than a bout of exercise a day, an easy alternative is to increase movement in our daily activities, such as housework, gardening, walking or cycling as a mode of commute and taking the stairs. A recently published study by Duvivier et al. (in scientific journal Plos One) suggested that one hour of daily physical exercise cannot fully compensate for the negative effects of inactivity on risk factors for cardiovascular disease (insulin level and plasma lipids) if the rest of the day is spent sitting.
The Study
In this study, eighteen healthy young subjects, age 21±2 year old of normal BMI followed one of three randomly assigned physical activity regimes for four days. In the sitting regime, participants were instructed to sit 14 hr/day. In the exercise regime, participants were instructed to sit 13 hr/day and to substitute 1 hr of sitting with 1 hr of vigorous supervised bicycling. Lastly, participants in the minimal intensity physical activity regime were instructed to substitute 6 hrs sitting with 4 hr walking and 2 hr standing. All regimes were instructed to walk 1 hr/day, stand 1 hr/day and spend 8 hr/day sleeping or supine. The exercise and minimal intensity physical activity regime had the same daily energy expenditure. During the four days of regime, physical activity monitors were continuously worn (24 hours a day) by the participants.
Figure 1. Time spent on different activities per regime.
Graphical overview of the three regimes followed by the participants and time spent in different activity categories (sleeping, sitting, standing, cycling and activity (walking).
Results
Results of the study showed that reducing inactivity by increasing the time spent walking/standing is more effective in lowering blood cholesterol and lipid levels, when energy expenditure is kept constant. Moving more everyday and reducing prolonged sitting time is much more effective than a bout of one hour intensive cycling exercise. It also demonstrated that the negative effects of extensive sitting on our health cannot be compensated by an hour of exercise per day. Therefore apart from including exercise in our lifestyle, health advice should also focus on decreasing sedentary time and moving more.
One of the strategies to keep track of daily movements is the use of an activity tracker. Physical activity trackers have gained popularity to assist individuals in monitoring their level of activity and reaching their daily activity goals.
Reference:
Duvivier BMFM, Schaper NC, Bremers MA, van Crombrugge G, Menheere PPCA, Kars M, et al. (2013) Minimal Intensity Physical Activity (Standing and Walking) of Longer Duration Improves Insulin Action and Plasma Lipids More than Shorter Periods of Moderate to Vigorous Exercise (Cycling) in Sedentary Subjects When Energy Expenditure Is Comparable. PLoS ONE 8(2): e55542.
Download the article here.
For more information about this study, please contact:

Bernard Duvivier, MD
Department of Internal Medicine
Department of Human Movement Sciences
Maastricht University Medical Centre
Maastricht, The Netherlands
bernard.duvivier@maastrichtuniversity.nl