
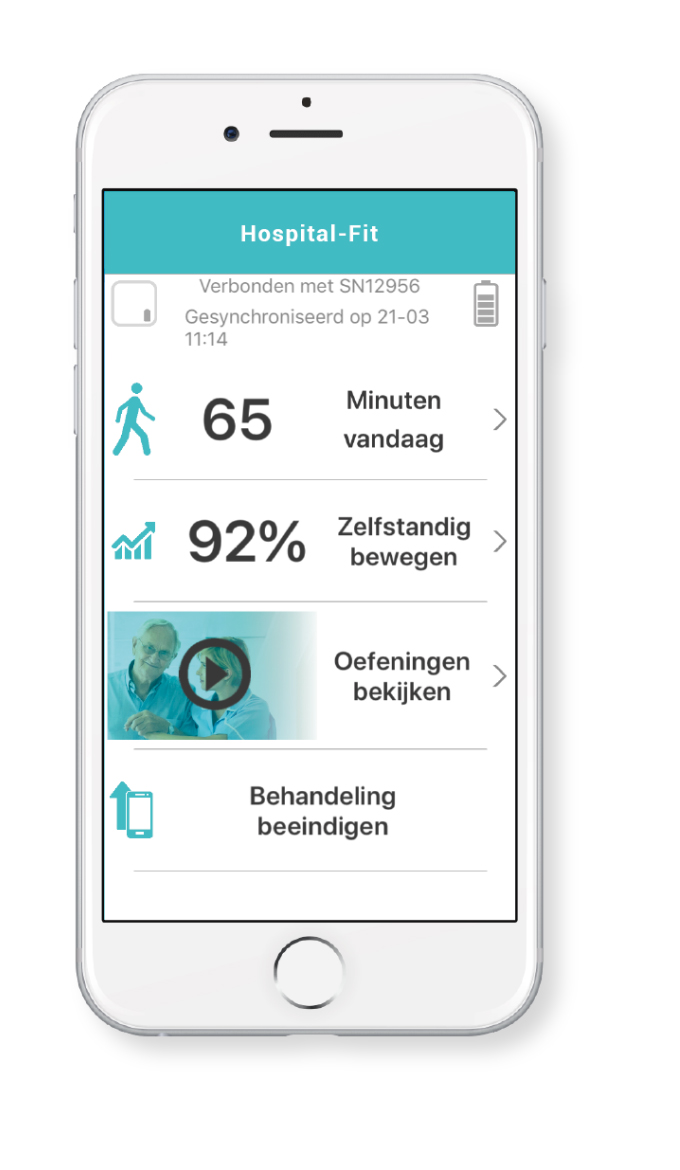
Hospital Fit is a digital health tool designed to support hospitalized patients and their physical therapists on their way to an active recovery
The patients’ condition can worsen during hospitalization. When patients are hospitalized the brain function, muscle strenght and stamina decreases in 80% of all cases. Hospital Fit aims to prevent this decrease as much as possible and give the patient advice on staying as fit as possible during his/her admission. By stimulating the patient’s activities, they can optimize of their own recovery process.
The tracking of patient’s activities provides useful insights for patients as well as healthcare professionals. With a user-friendly dashboard, patients get access to monitor daily activity and improve recovery. Patients are being incentivized to boost their physical activity during the day. Together with the professional healthcare providers they can determine which exercises will suit them and provide a personalized training schedule for the patient.
UMCRadboud on the importance of physical activity during hospitalization (dutch)
Our proposition
Incentify patients
Provide self-management support
for your patient and incentive for sufficient
daily activity in the hospital.
Monitor progress
Get access to a personal recovery
toolbox where each patient can
monitor their progress.
Personalized
You can create a personalized training
schedule for the patient. The plan is
available at any moment.
24/7 guidance
Most hours of the day you are not at
your patients side. Guide your patient
24hr/day with hospital fit.
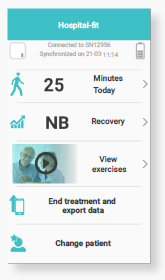
Activity monitoring
the activity monitor measures the
patients’ daily activity. Sufficient
activity improves recovery.
Earlier discharge
view your progress and achieve targets
together to make earlier discharge
possible.
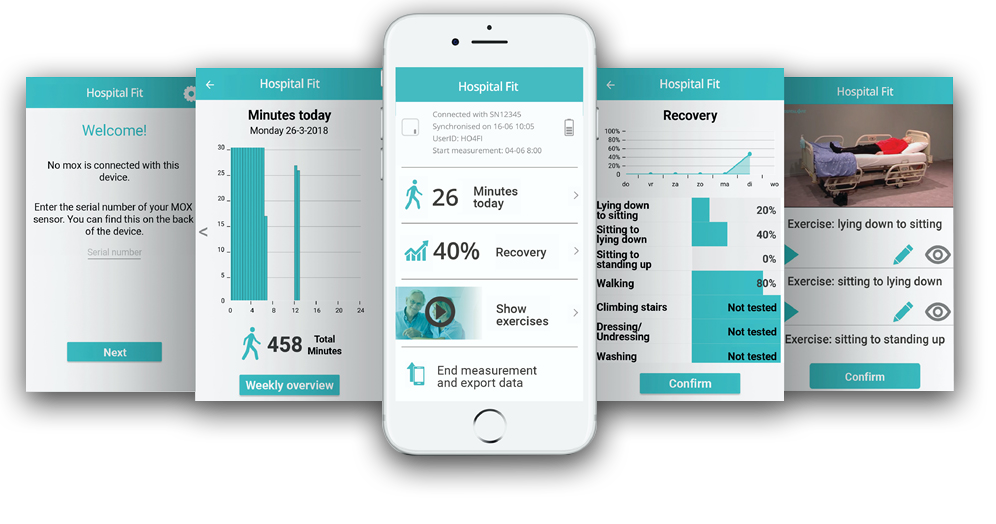
Inside the app
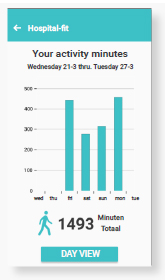 Activity
Activity
Your activities and exercise will be made visible in the movement
overview. Detailled daily overviews and a week summary are provided.
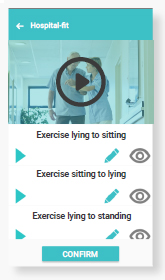 Exercise
Exercise
a set of video exercises, specifically aimed at functional recovery, can be
selected for the patient. Provide notes if needed. 25 video’s included.
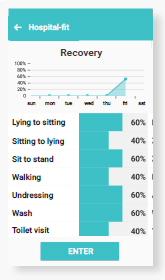 Recovery
Recovery
The amount of functional recovery can be scored and communicated to the patient. The patient can see progress achieved.
 Switch
Switch
Patients can see their own data, the therapist can switch between patients during daily visits.
New features Hospital Fit 2.0
✓ Objective insight into exercise behavior for patients and therapists
✓ Multidisciplinary stimulation of physical activity
✓ Tailor-made exercise program
✓ Ability to set goals
✓ Database with exercise videos for functional movement, muscle strength and stamina
✓ Provide insight into the degree of independence.
✓ Provide information about the importance of exercise
✓ Reminder function (4x per day)
✓ Export data to online database
✓ Anonymized data available for research purposes
✓ Link with the patient’s EPD
MOX activity monitor
Why use medical graded accelerometers?
The MOX wireless accelerometry sensor is a medical grade, wearable accelerometer that has been validated for the measurement of various
levels of activity in healthy persons, elderly and patients with a chronic condition.
- Fully Compliant to Medical Devices Directive
- Providing insight into exercise behavior
- Real-time feedback
- Validated on hospital patients.
- High comfort for patients and waterproof

Validation
Our pilot study: Smartphone App with an Accelerometer Enhances Patients’ Physical Activity Following Elective Orthopedic Surgery
Abstract: Low physical activity (PA) levels are common in hospitalized patients. Digital health tools could be valuable in preventing the negative effects of inactivity. We therefore developed Hospital Fit; which is a smartphone application with an accelerometer, designed for hospitalized patients. It enables objective activity monitoring and provides patients with insights into their recovery progress and offers a tailored exercise program. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential of Hospital Fit to enhance PA levels and functional recovery following orthopedic surgery. PA was measured with an accelerometer postoperatively until discharge. The control group received standard physiotherapy, while the intervention group used Hospital Fit in addition to physiotherapy. The time spent active and functional recovery (modified Iowa Level of Assistance Scale) on postoperative day one (POD1) were measured. Ninety-seven patients undergoing total knee or hip arthroplasty were recruited. Hospital Fit use, corrected for age, resulted in patients standing and walking on POD1 for an average increase of 28.43 min (95% confidence interval (CI): 5.55–51.32). The odds of achieving functional recovery on POD1, corrected for the American Society of Anesthesiologists classification, were 3.08 times higher (95% CI: 1.14–8.31) with Hospital Fit use. A smartphone app combined with an accelerometer demonstrates the potential to enhance patients’ PA levels and functional recovery during hospitalization.
Keywords: activity monitoring; physical activity; functional recovery; hospitalization; mHealth;wearable sensors; arthroplasty; physiotherapy
Optimization and Validation of a Classification Algorithm for Assessment of Physical Activity in Hospitalized Patients
Abstract: Low amounts of physical activity (PA) and prolonged periods of sedentary activity are common in hospitalized patients. Objective PA monitoring is needed to prevent the negative effects of inactivity, but a suitable algorithm is lacking. The aim of this study is to optimize and validate a classification algorithm that discriminates between sedentary, standing, and dynamic activities, and records postural transitions in hospitalized patients under free-living conditions. Optimization and validation in comparison to video analysis were performed in orthopedic and acutely hospitalized elderly patients with an accelerometer worn on the upper leg. Data segmentation window size (WS), amount of PA threshold (PA Th) and sensor orientation threshold (SO Th) were optimized in 25 patients, validation was performed in another 25. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and (absolute) percentage error were used to assess the algorithm’s performance. Optimization resulted in the best performance with parameter settings: WS 4 s, PA Th 4.3 counts per second, SO Th 0.8 g. Validation showed that all activities were classified within acceptable limits (>80% sensitivity, specificity and accuracy, ±10% error), except for the classification of standing activity. As patients need to increase their PA and interrupt sedentary behavior, the algorithm is suitable for classifying PA in hospitalized patients.
Keywords: physical activity; accelerometers; algorithm; validation; hospitalized patients
Address and contact info
Maastricht Instruments BV
Universiteitssingel 50
6229 ER Maastricht
+31 43 388 4000
email@maastrichtinstruments.com